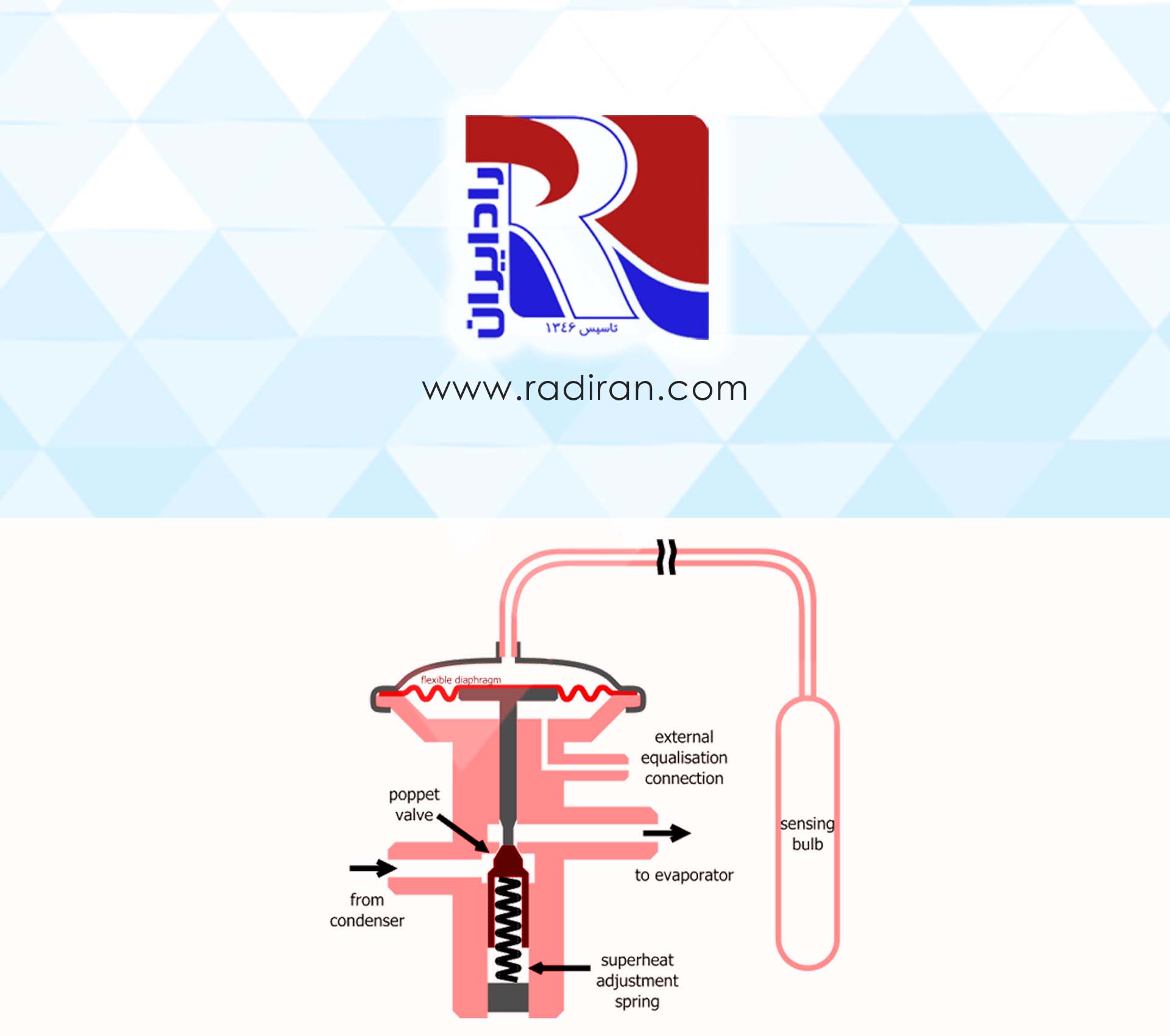
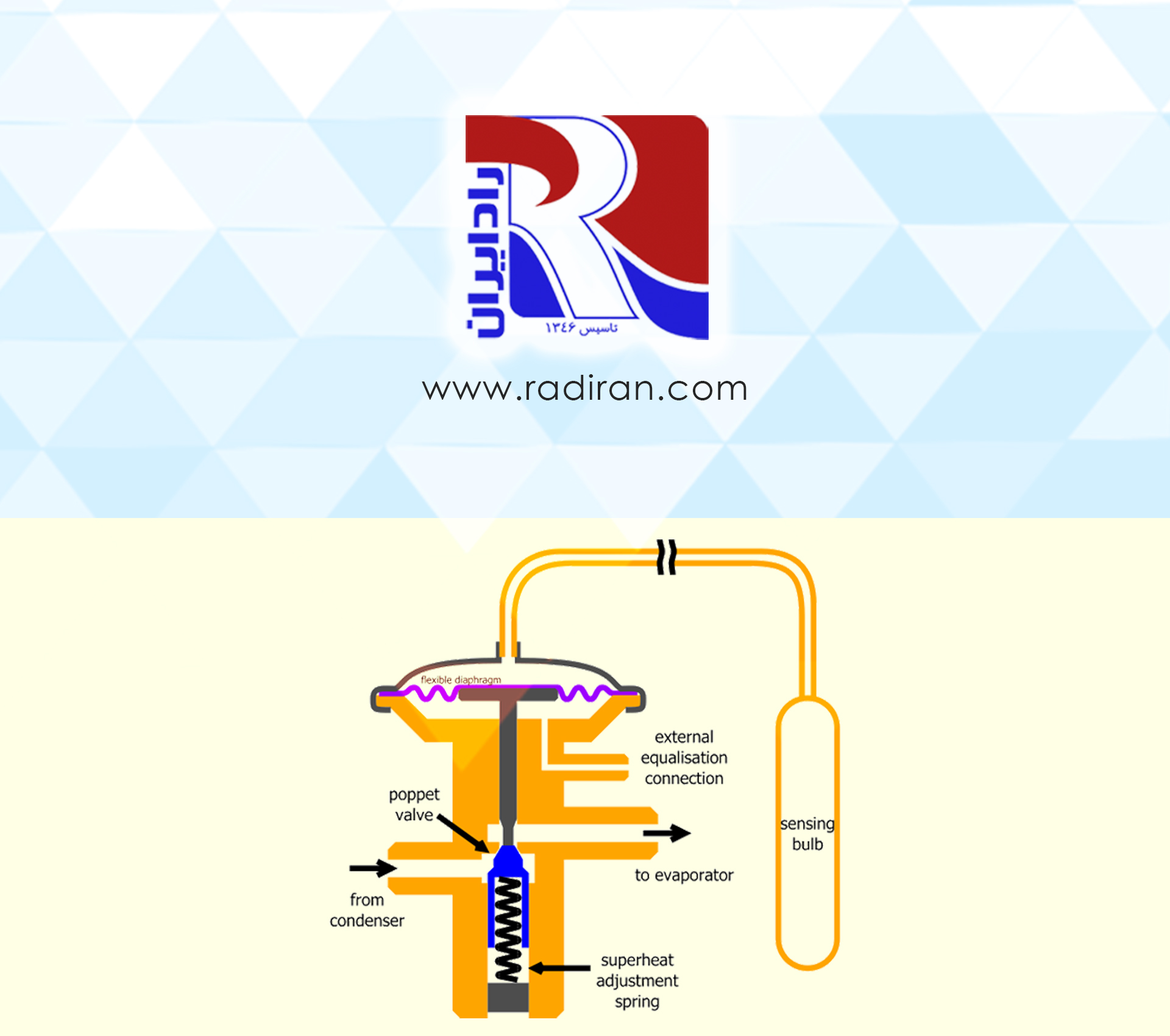
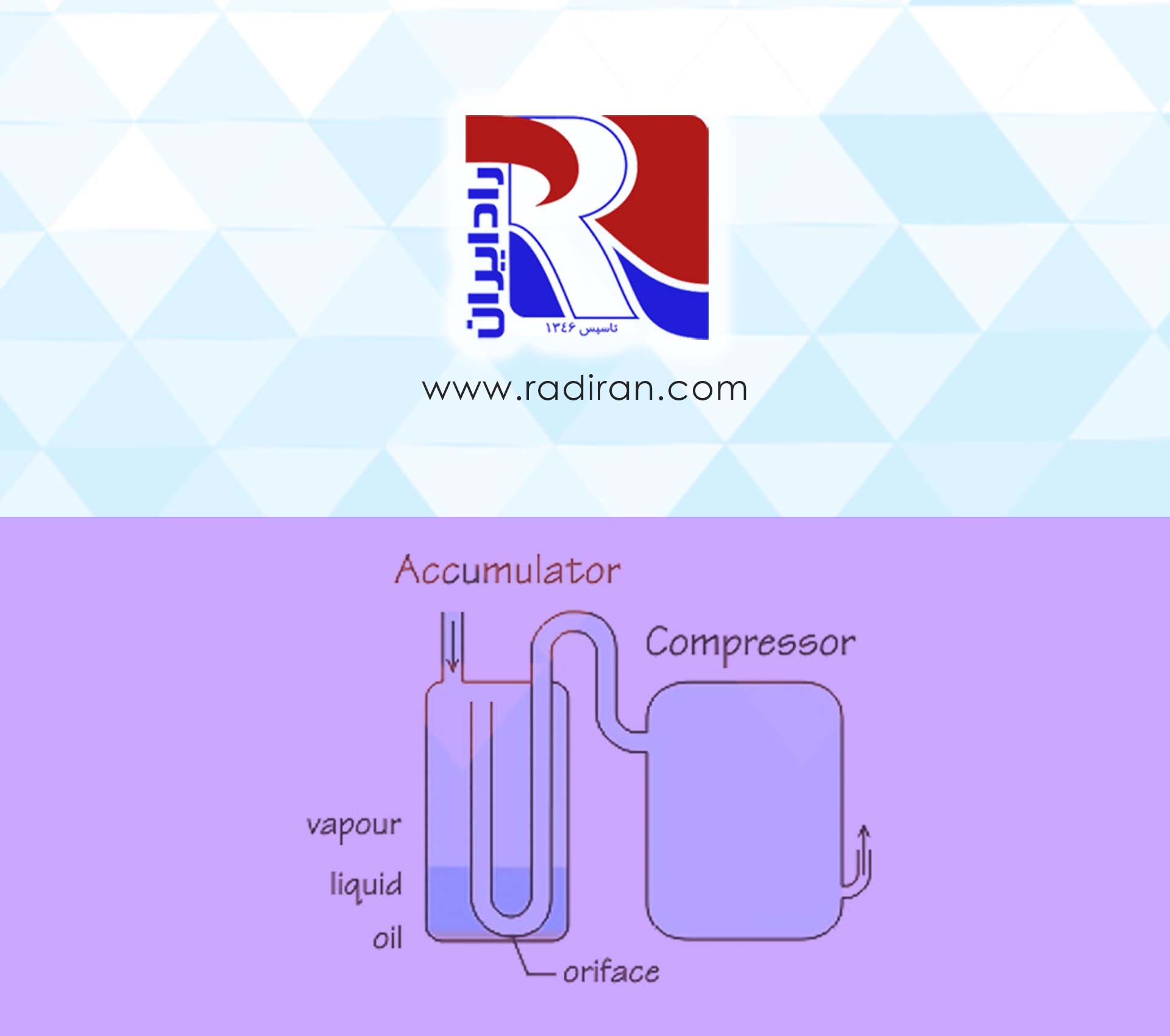
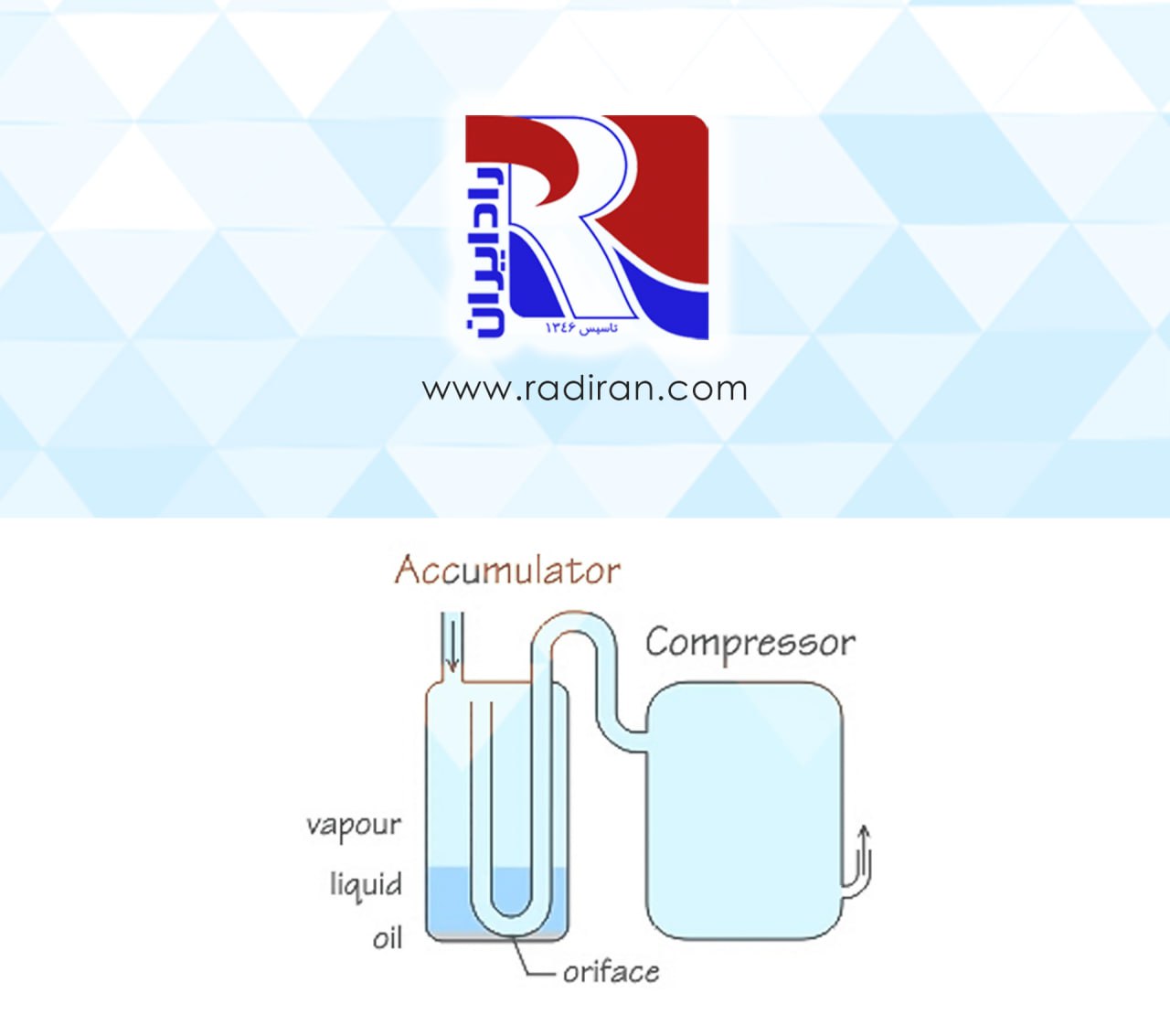
Sight Glass
Definition of Sight Glass A sight glass is a transparent tube that allows users to observe the fluid flowing through it. This device is used for analyzing conditions in industrial equipment and chemical reactors. Materials and Features Sight glasses are usually made of very durable glass that does not get damaged under specific conditions. The glass is strengthened through a thermal process, and an additional protective coating is applied to guard against chemical substances. These features make the glass resistant to stress, reducing the likelihood...