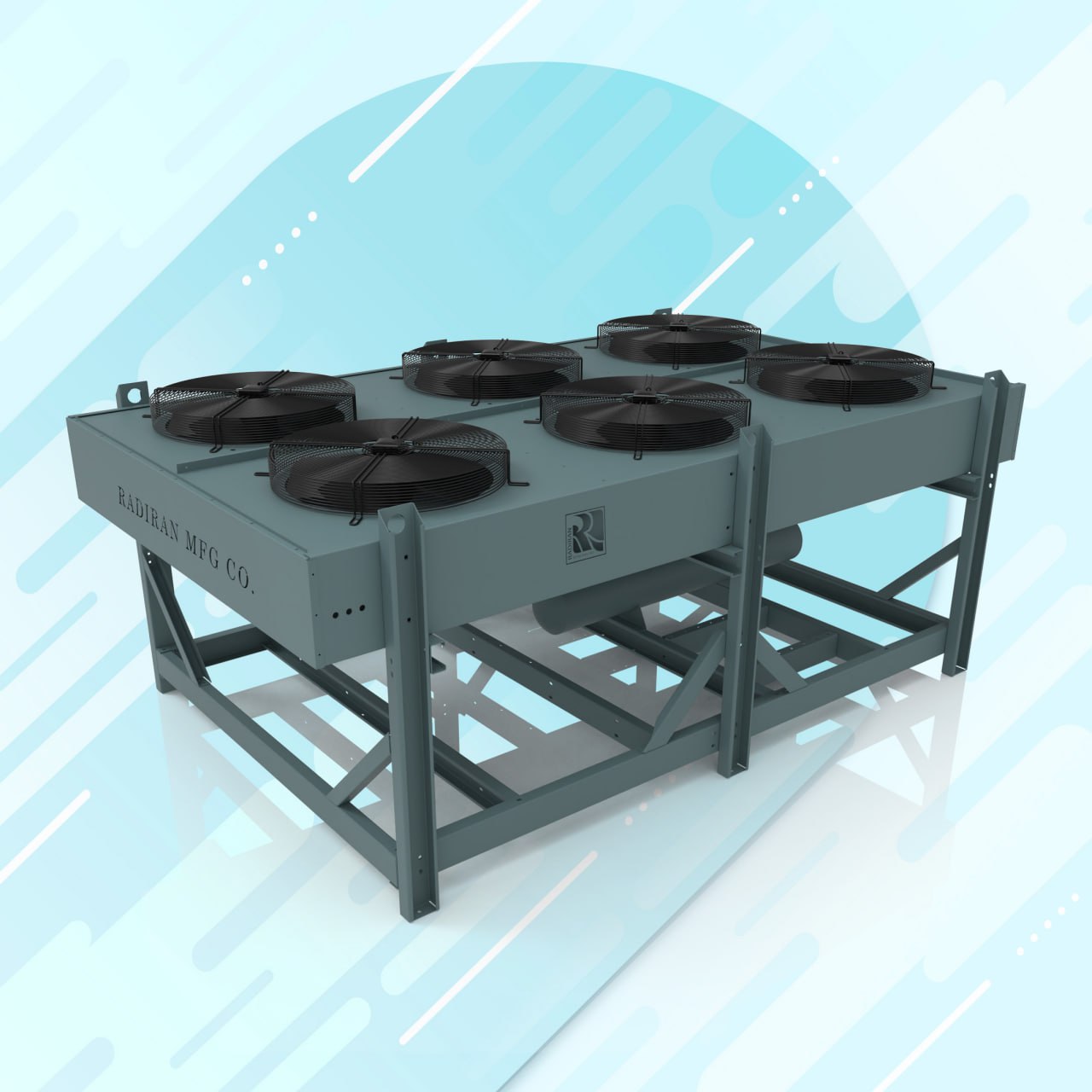
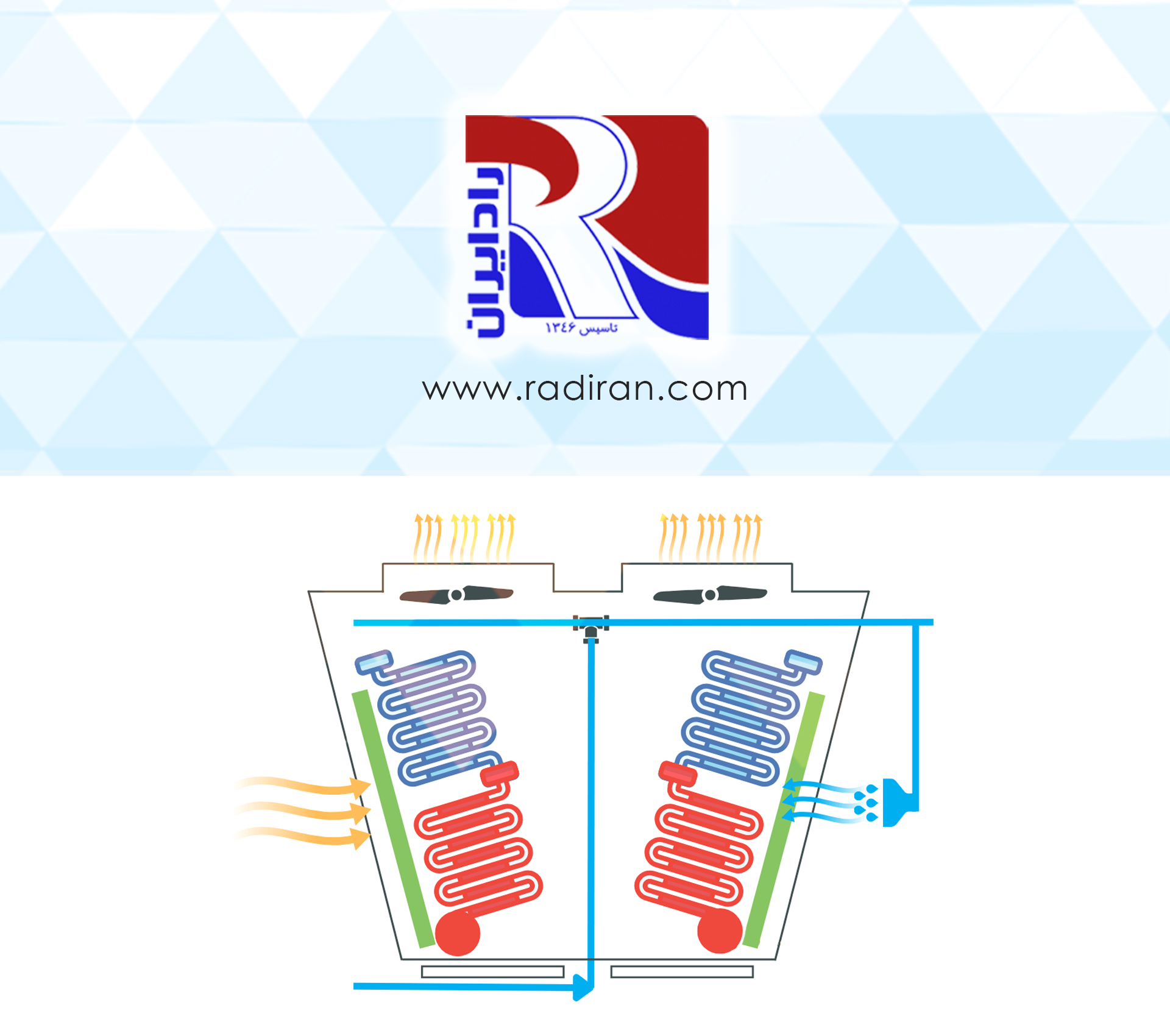
Dry cooler (air cooler) and its role in water conservation?
A dry cooler is essentially an air cooled condenser similar to the condenser of a chiller, but instead of refrigerant flowing through its tubes, any hot fluid can circulate—e.g., water, ethylene glycol/water mixtures, propylene glycol/water mixtures, chemical fluids, etc. A dry cooler consists of finned coils and fans; the hot fluid flows in a fully closed loop and rejects heat to the air that the fans force across the finned coils, thereby cooling the fluid. Dry coolers replace evaporative cooling...