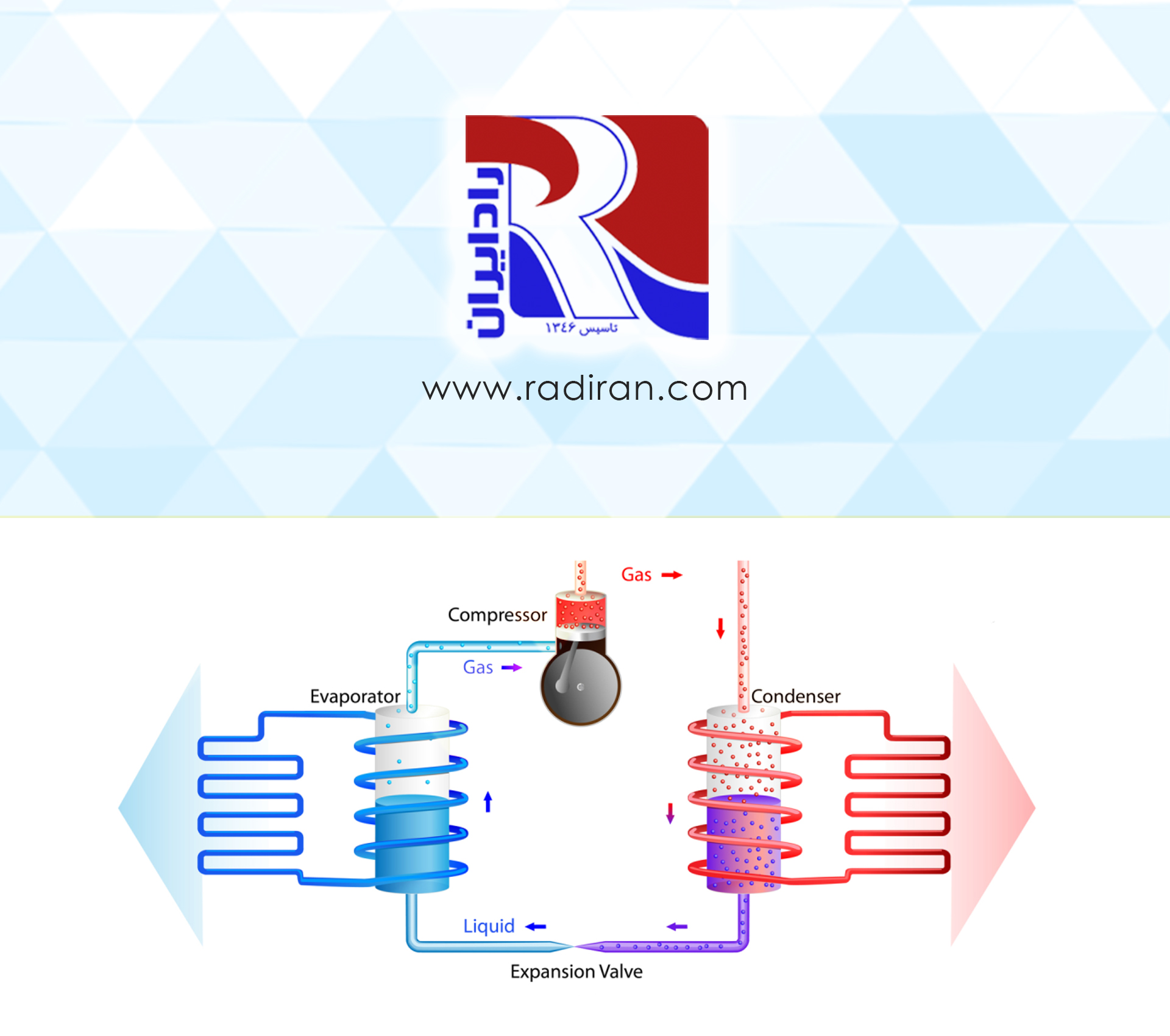
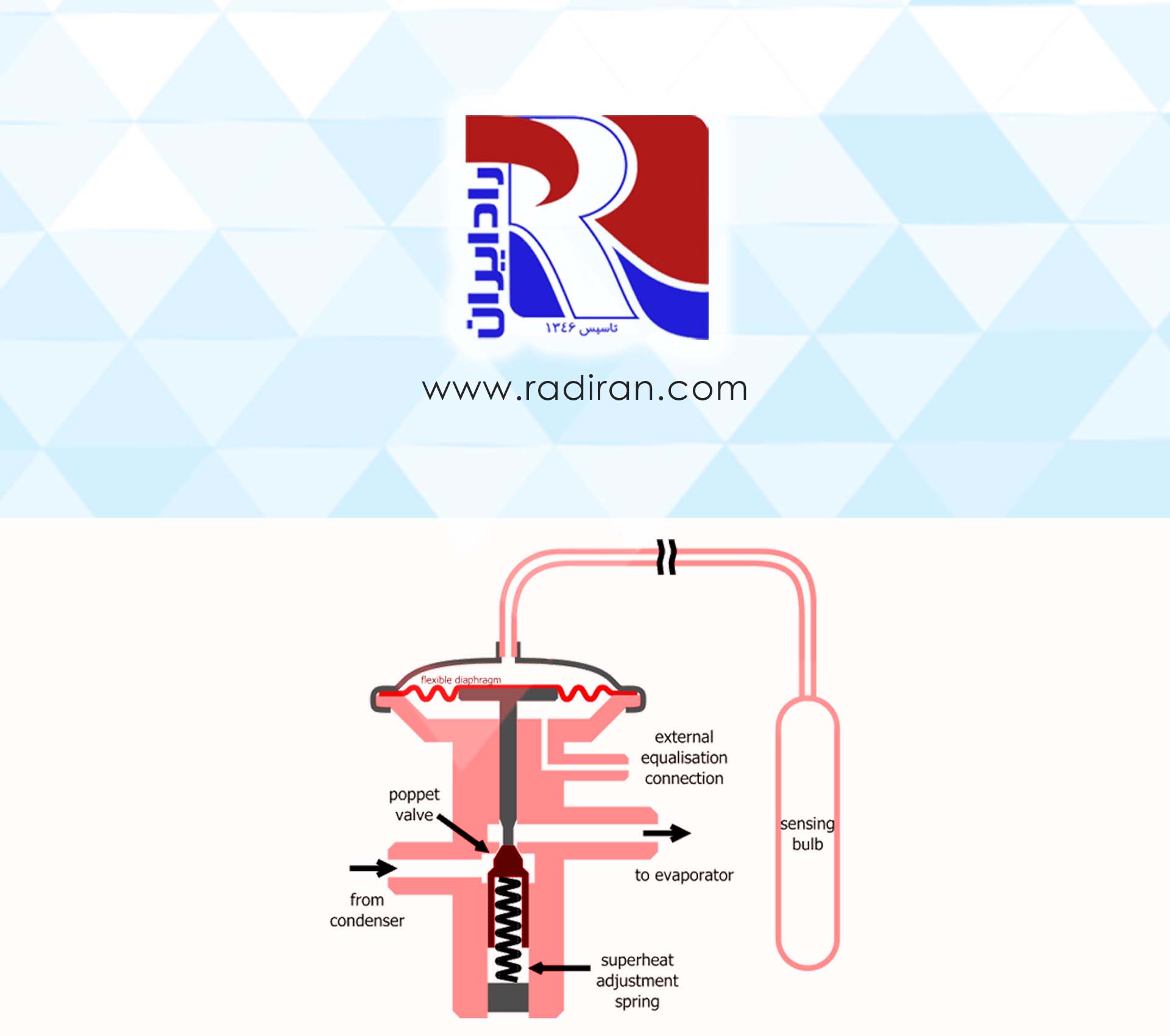
Service Valves in Refrigeration Systems
systems and explains the role of each in the proper functioning of the system: Hand Valve: Hand valves are used for manual control of refrigerant flow in the piping lines. They allow manual opening or closing of the flow and are used during system maintenance and repair. Suction Service Valve: These valves are located on the suction line of the compressor and are used to facilitate servicing and repairs. Discharge Service Valve: Discharge service valves are placed on the compressor discharge line and, similar to suction...