Subcooling and Superheating Definition
- Definition of Subcooling
- Subcooling refers to a liquid whose temperature is lower than its saturation point.
- Process of Subcooling
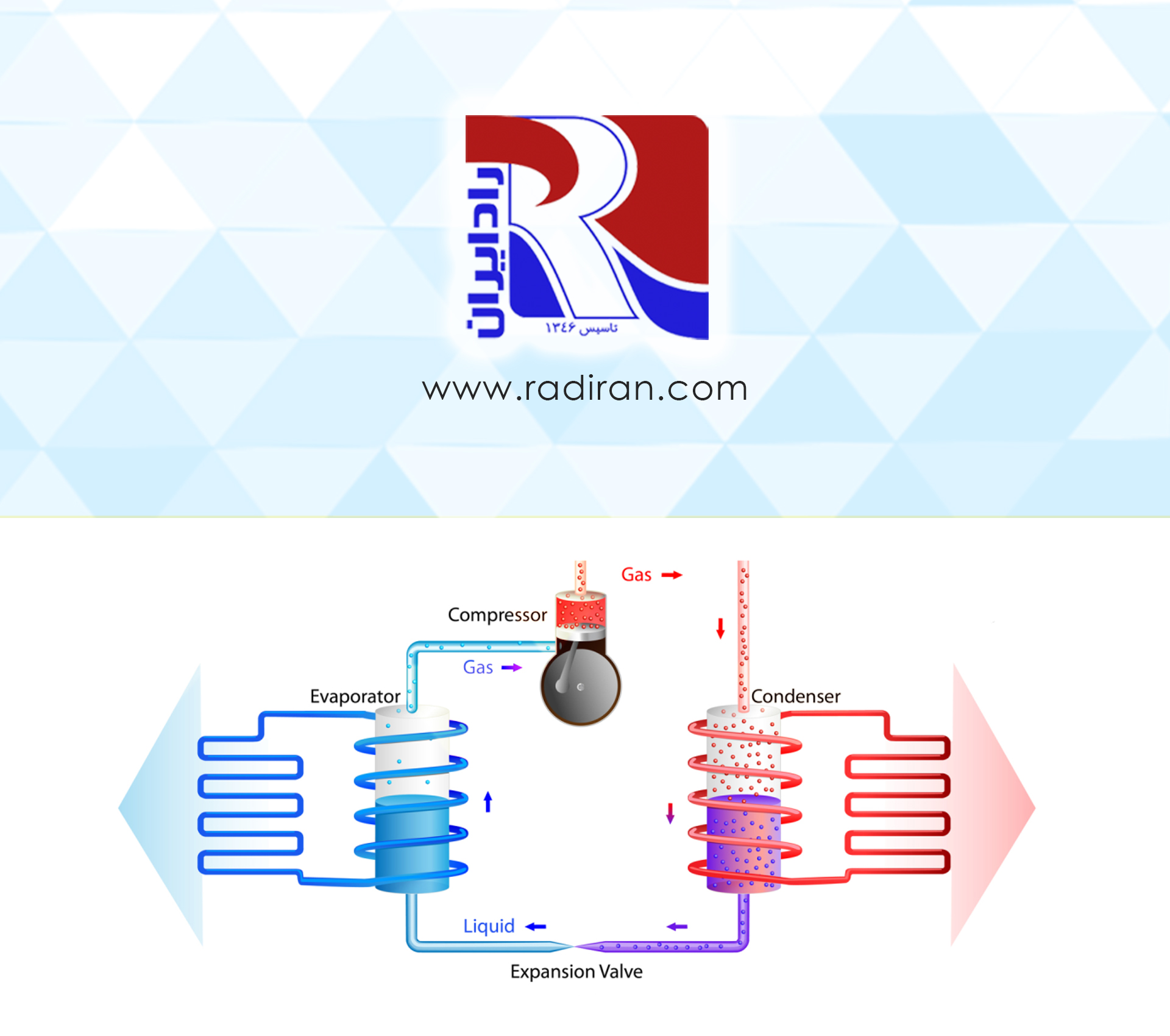
- Subcooling and condensation occur in the condenser.
- The use of subcooling is for transferring refrigerant from the condenser to the thermostatic expansion valve in liquid form.
- Mechanism of Refrigeration Systems
- The refrigerant absorbs heat and releases it to the environment after leaving the compressor and reaching the condenser.
- The temperature decreases in the condenser, and the refrigerant transitions to the liquid phase.
- Advantages of Subcooling
- Increased capacities with reduced temperatures.
- Energy savings and reduced refrigerant flow rates.
- The possibility of using smaller pipes in the system.
- Auxiliary Cooling Systems
- Types of condensers:
- Water-cooled condensers
- Air-cooled condensers
- Evaporative condensers
- Calculation of Subcooling
- Formula: Subcooling = Boiling Point – Current Temperature
- Practical Example
- An example with refrigerant R22 and the cooling process in the condenser.
Definition of Superheat
- Superheat refers to the state where vapor is heated above its boiling point.
- Example: The refrigerant boils at 40 degrees Fahrenheit and is heated to 50 degrees; in this case, the superheat is 10 degrees.
- Process of Superheat
- It ensures that the refrigerant is completely converted to vapor before entering the compressor.
- It prevents damage to the compressor that could result from low liquid levels.
- Formula for Calculating Superheat
- Superheat = Current Temperature – Boiling Point
- Importance of Superheat and Subcooling
- These two measurements are important for determining the performance of HVAC systems.
- The benefits of monitoring these measurements:
- Improved system efficiency
- Easy and quick problem detection
- Prevention of overheating
- Operational Concerns
- Inefficiency is usually due to improper refrigerant levels.
- Technicians help diagnose problems by checking superheat and subcooling.
- Overheating may result from low refrigerant levels, damaging the compressor and potentially leading to costly repairs.