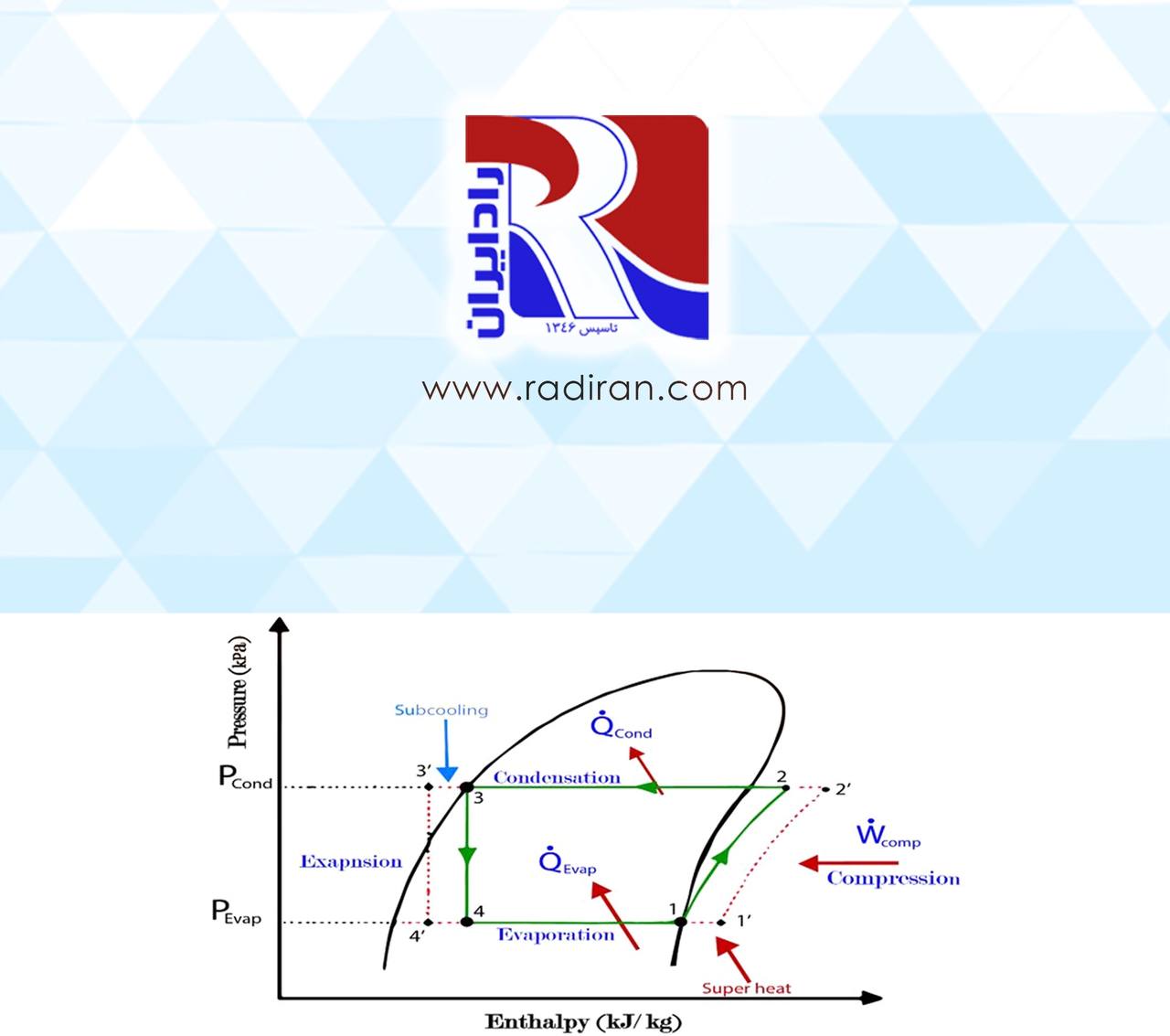
Subcooling and superheating
In refrigeration cycles, subcooling and superheating play important roles in optimizing system efficiency and performance. In fin tube coils, which are common in air conditioning and refrigeration systems, these concepts are particularly relevant. Radiran with over 50 years of experience in manufacturing coils and HVAC equipment, in this essay illustrates the subcool and superheat systems.
Subcooling occurs after the refrigerant has undergone condensation but before it enters the expansion valve. During subcooling, any remaining vapor in the refrigerant is condensed into a liquid. This process ensures that the refrigerant entering the expansion valve is in its liquid state, which enhances the efficiency of the expansion process. Subcooling also helps prevent flashing or the formation of vapor bubbles in the expansion valve, which can disrupt the proper functioning of the system. By lowering the refrigerant’s temperature below its saturation point at the condenser pressure, subcooling increases the system’s refrigerating effect and improves the overall performance.
On the other hand, superheating occurs after the refrigerant has evaporated completely in the evaporator coil but before it enters the compressor. During superheating, any additional heat absorbed by the refrigerant vapor increases its temperature above its saturation point at the evaporator pressure. This ensures that only superheated vapor enters the compressor, preventing the compressor from handling any liquid refrigerant, which could cause damage. Superheating also helps maintain the compressor’s efficiency by ensuring a consistent flow of gas and preventing liquid slugging, a condition where liquid refrigerant enters the compressor and causes mechanical damage.
In fin tube coils, subcooling and superheating are controlled through proper design and sizing of the components, as well as accurate temperature and pressure regulation. The fin design enhances heat transfer between the refrigerant and the surrounding air, facilitating the subcooling and superheating processes. Additionally, fin tube coils are often equipped with expansion devices and sensors to regulate the flow of refrigerant and maintain optimal operating conditions.
In summary, subcooling and superheating are essential aspects of refrigeration cycles in fin tube coils, helping to improve efficiency, prevent damage to components, and ensure reliable operation. Proper design, sizing, and control are key to maximizing the benefits of these processes in air conditioning and refrigeration systems. In Radiran we consider every aspect of coil design and system performance, using subcool, superheat and other technologies to optimize the products.