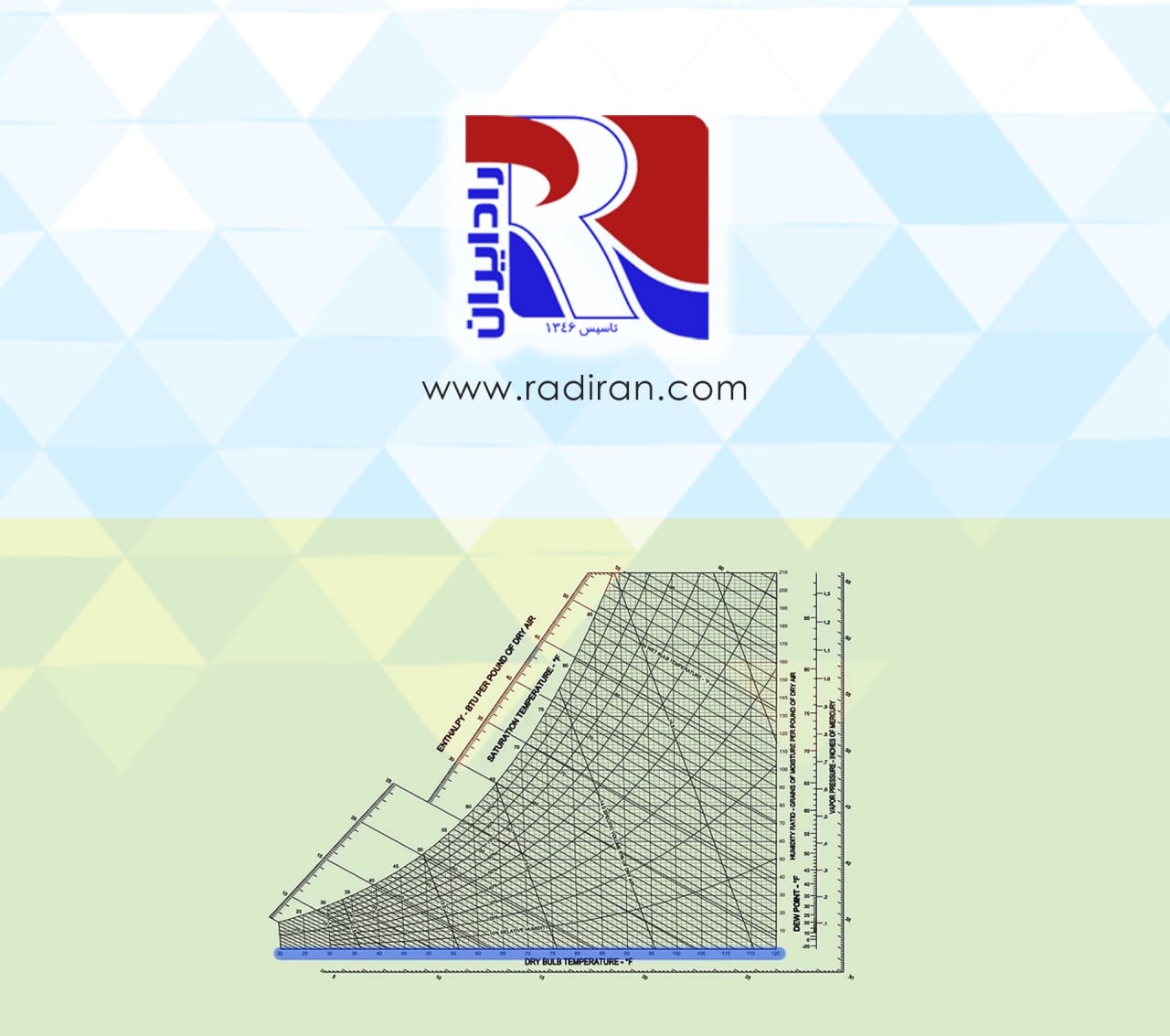
Psychrometric Chart and Air Characteristics
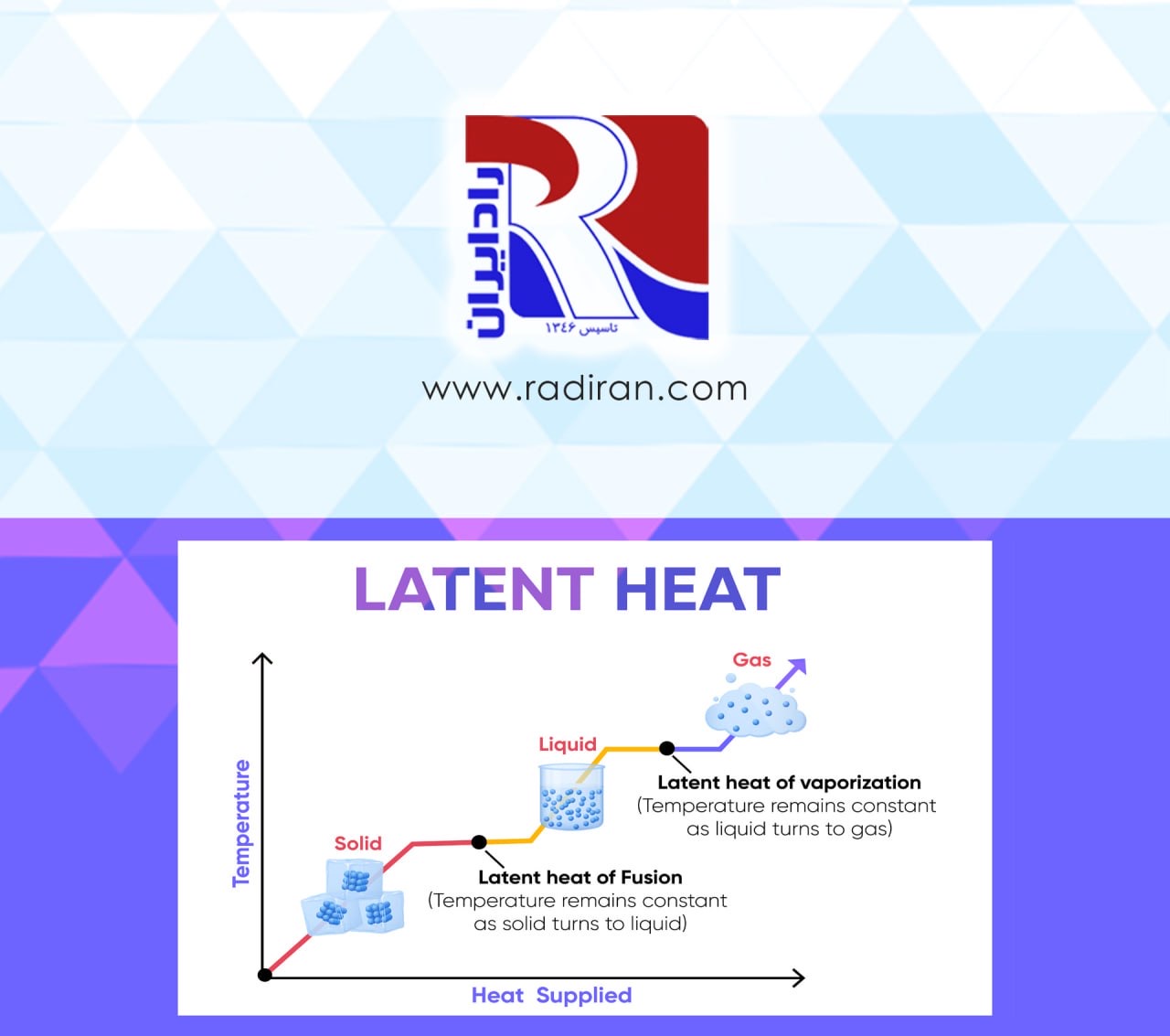
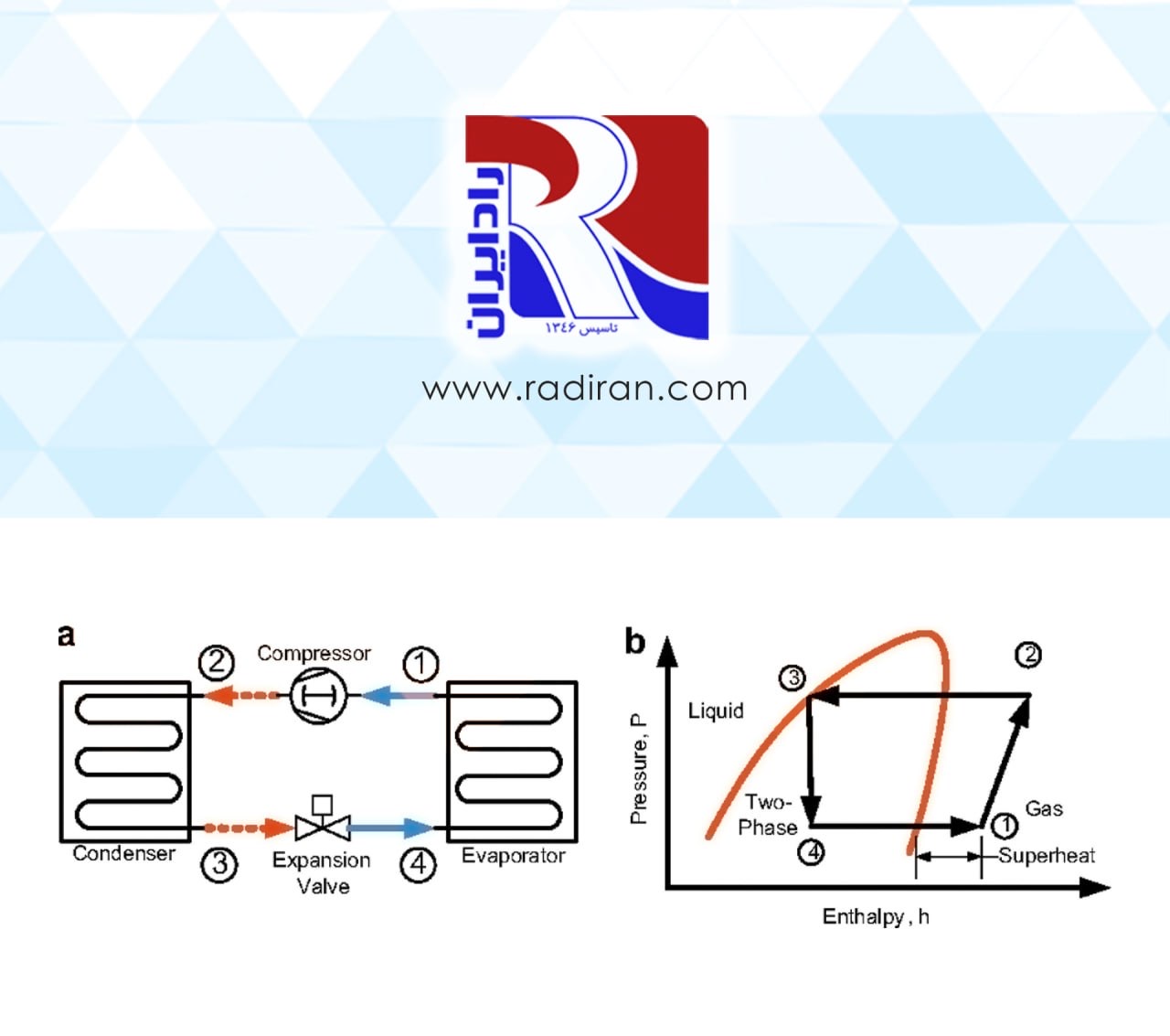
A psychrometric chart presents physical and thermal properties of moist air in a graphical form. It can be very helpful in troubleshooting and finding solutions to greenhouse or livestock building environmental problems. Understanding psychrometric charts can help you visualize environmental control concepts, such as why heated air can hold more moisture or, conversely, how allowing moist air to cool will result in condensation. This article explains how characteristics of moist air are used in a psychrometric chart. Three examples are...