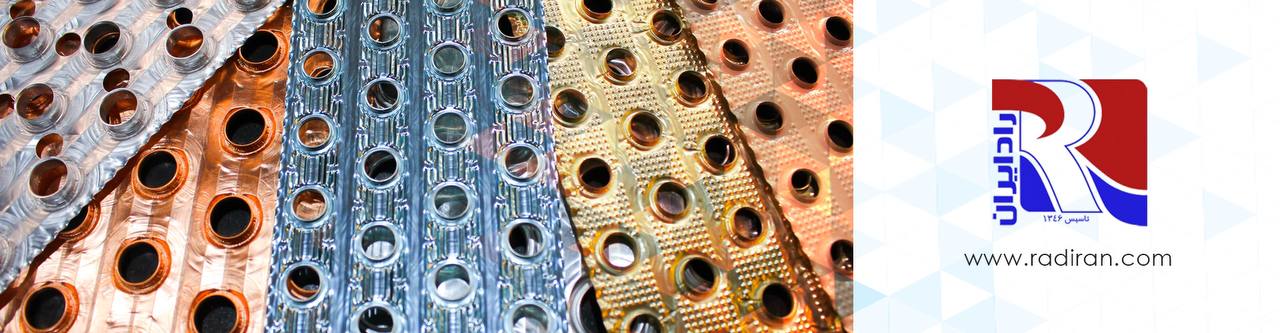
Gold fin and Blue fin
Gold fin and blue fin are types of coatings applied to the fins of heat exchanger coils, commonly used in air conditioning and HVAC systems. 1- Gold Fin: Gold fin, also known as golden hydrophilic fin, typically refers to a type of corrosion-resistant coating applied to the aluminum fins of heat exchanger coils. The "gold" color comes from the protective coating, which is often a hydrophilic layer. This coating helps prevent corrosion, enhances heat transfer efficiency, and discourages the...