Logarithmic Mean Temperature Difference
1. Definition of Logarithmic Mean Temperature Difference (LMTD)
The logarithmic mean temperature difference is not an arithmetic average but a logarithmic one, used to calculate the temperature difference between two fluid streams in a heat exchanger where temperatures gradually change.
The general formula is:
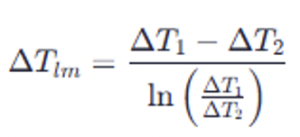
ΔT1= temperature difference at the beginning of the path (e.g., hot fluid temperature minus cold fluid temperature at the inlet)- ΔT2 = temperature difference at the end of the path (e.g., hot fluid temperature minus cold fluid temperature at the outlet)
- ln = natural logarithm
2. Explanation and Application in HVAC
In HVAC systems, heat exchangers (such as radiators, heating or cooling coils, chillers, and boilers) transfer heat between two fluids, usually water and air.
- Suppose in a heat exchanger two fluids (like water and air) flow, with temperatures changing along the exchanger.
- To calculate heat transfer, we need the average temperature difference between the fluids.
- Since temperature changes along the path, using only the difference at the inlet or outlet is inaccurate.
- LMTD provides a more precise average temperature difference and is the basis for heat transfer calculations in designing and analyzing heat exchangers.
3. Categories and Conditions of Use
- Parallel Flow Heat Exchanger: Both fluids flow in the same direction. The temperature difference is higher at the inlet and decreases along the flow.
- Counterflow Heat Exchanger: Fluids flow in opposite directions. Temperature difference at both ends is important, making LMTD especially relevant.
- Crossflow and Complex Flows: In many such cases, LMTD is adjusted with correction factors.
4. Simple Numerical Example
Suppose:
- Temperature difference at the beginning: ΔT1=30∘CΔT1=30∘C
- Temperature difference at the end: ΔT2=10∘CΔT2=10∘C
Then the logarithmic mean temperature difference:
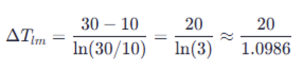
This value represents the effective temperature difference to be used in heat transfer calculations.
5. Importance of LMTD in HVAC
- Accuracy in designing coils and heat exchangers.
- Precise determination of heat transfer capacity.
- Energy consumption optimization and suitable equipment selection.
- Predicting system performance and increasing equipment lifespan.