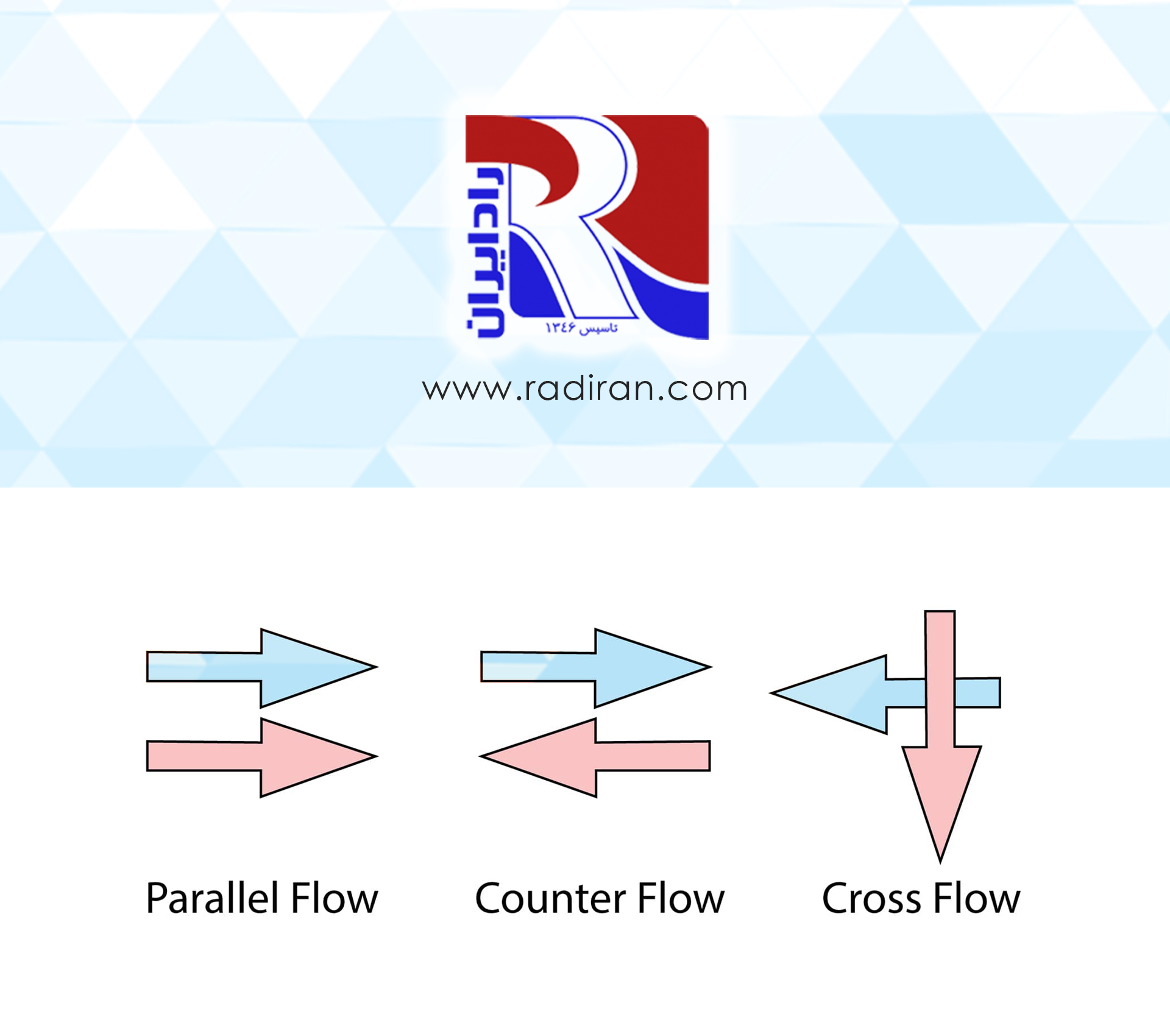
Introduction and Importance of Fin-and-Tube Coil Maintenance
Fin-and-tube coils (Fin and Tube Coils) are key components in HVAC systems, chillers, heat exchangers, and various industrial equipment. Maintaining the condition and performance of these heat-transfer assemblies requires adherence to specialized cleaning and maintenance procedures. Specialized Cleaning Procedures 1. Initial Inspection • Use high-resolution borescopes for internal visual inspection. • Assess contamination and corrosion level of aluminum fins. • Examine copper tubes for scale deposition and corrosion. 2. Preparation • Isolate power and gas supply. • Completely drain the working fluid from the system. • Install protective covers...