Defrost Process – Part two
Air defrosting
In refrigeration, air defrost is an effective method of combating ice build-up in evaporators. This process uses the air in the chamber itself to defrost the frost efficiently.
Its suitability is intensified in chambers above 4ºC, as at lower temperatures its effectiveness is reduced.
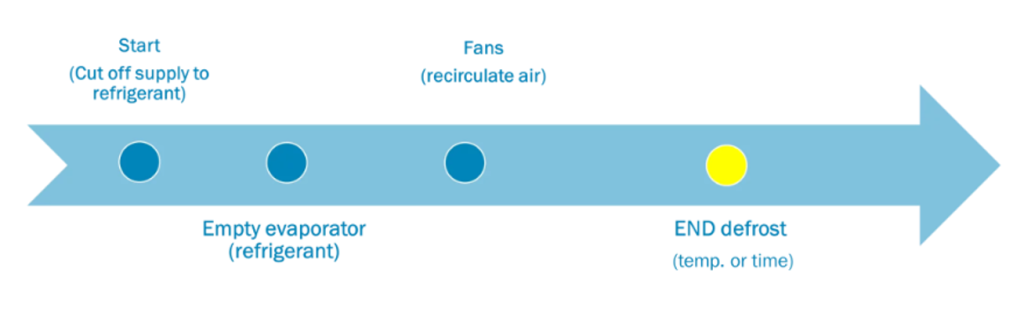
The system starts with the closing of the liquid solenoid valve, which stops the refrigerant flow to the evaporator and to be emptied by the compressor until it stops. In this case the fans recirculate the air in the chamber passing it through the coil, facilitating the defrosting of the accumulated ice. The defrost process ends automatically, either by detection of the defrost set point temperature by means of a probe or by compliance with the time set in the system, ensuring that the evaporator returns to normal operation without thermal shocks with a smooth transition to the resumption of refrigeration activity.
Air defrost is useful in environments that require meticulous humidity control, such as fruit and vegetable chambers or warehouses. It is also common in workrooms. Specialised INTARCON equipment, such as those in bottled wine cellars or barrels, and compact high-temperature industrial equipment, such as the R-290 superblock, use this method. In this way, they optimise the preservation environment and maintain the energy and operational efficiency of the system.
Electric resistance defrosting
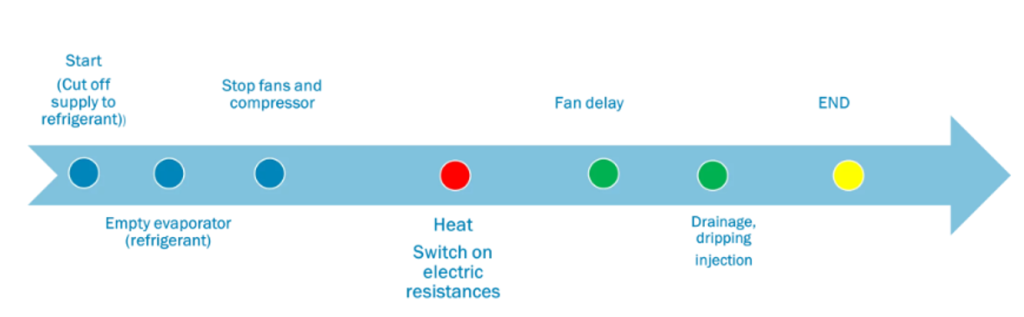
In refrigeration, electric resistance defrosting is used as an effective and controlled method of eliminating frost build-up on evaporators. This system consists of integrating electric heating elements directly inside the evaporator, with the objective of heating the affected surface and melting the frost.
Resistor defrosting is widely used in commercial and industrial applications where precise control of the defrosting process is required.
The process is close to standard, starting with shutting off the liquid solenoid valve to stop the refrigerant flow, followed by draining the compressor. The fans and compressors are then shut down simultaneously to prepare the system. Next, the electric heaters are activated, which are selected to provide the amount of heat required to melt the frost in the desired time. The delay times are set appropriately to ensure that the defrost process is completed efficiently.