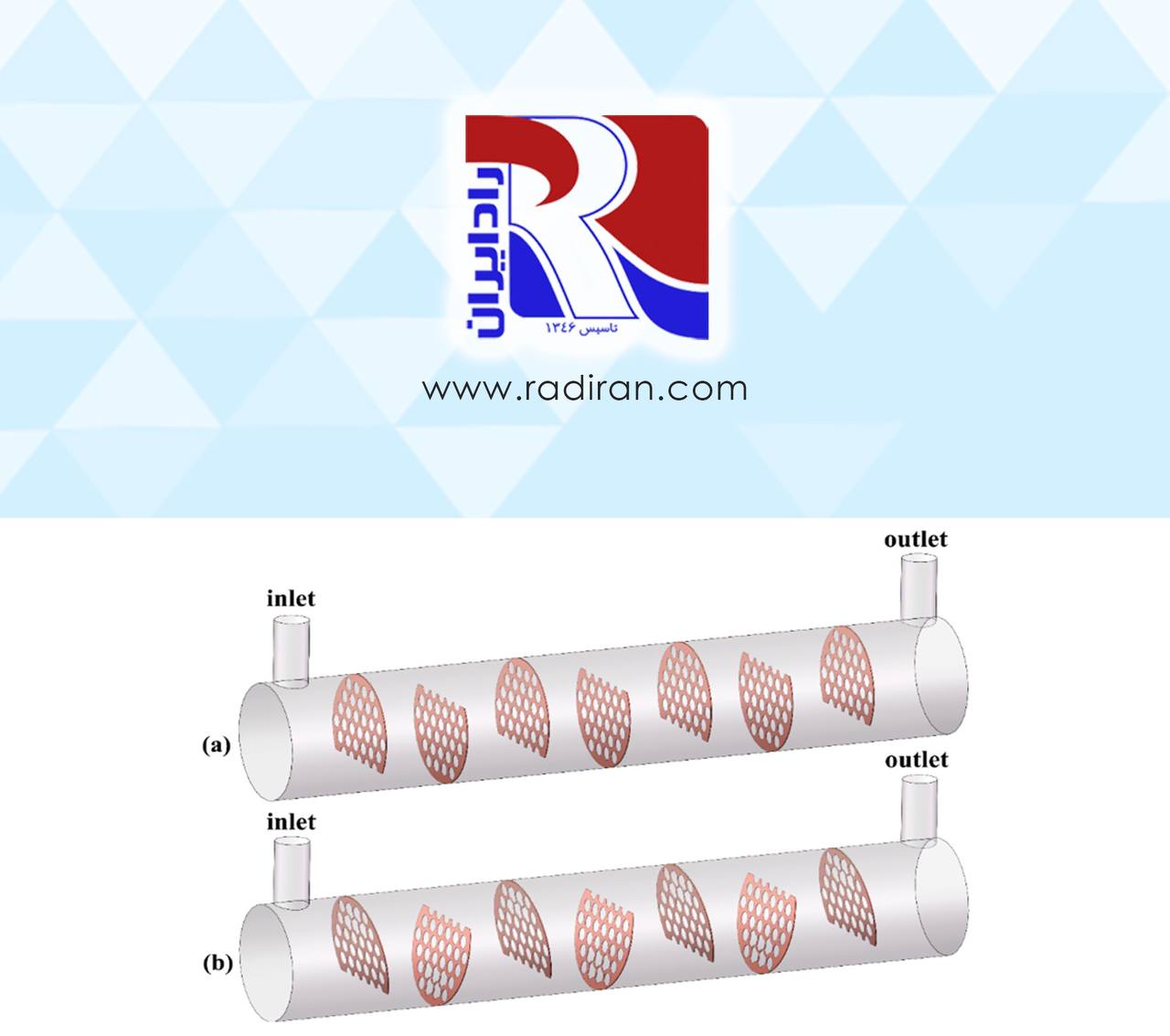
Baffles design parameters
Baffles play a crucial role in shell and tube heat exchangers. Design parameters for baffles in shell and tube heat exchangers include baffle spacing, baffle cut, baffle orientation, and baffle type. The spacing between baffles affects heat transfer and pressure drop.
- Baffle Spacing:
-Definition: Baffle spacing refers to the distance between adjacent baffles inside a shell and tube heat exchanger.
-Importance: Optimal spacing is crucial for balancing heat transfer efficiency and pressure drop. Closer spacing enhances heat transfer but increases pressure drop, while wider spacing reduces pressure drop but may compromise heat transfer.
- Baffle Cut:
-Definition: Baffle cut is the portion of the baffle that is removed to allow fluid flow through the shell side of the heat exchanger.
-Importance: Proper baffle cut is essential for controlling fluid distribution across the tubes. An appropriate cut ensures uniform flow and minimizes the risk of bypassing, which can lead to inefficient heat transfer.
- Baffle Orientation:
-Definition: Baffle orientation refers to the angle or direction in which baffles are installed within the heat exchanger.
-Importance: The orientation affects the cross flow patterns of the fluids. Common orientations are 90 degrees (perpendicular) or 45 degrees (diagonal). The choice depends on the specific heat exchanger design and the desired flow characteristics.
- Baffle Type:
-Definition: Baffle type refers to the specific design or shape of the baffles, with common types being segmental or helical.
-Importance: Different baffle types influence fluid dynamics and heat transfer characteristics. Segmental baffles provide good support for tubes, while helical baffles induce swirling flow, enhancing heat transfer. The choice depends on the application and performance requirements.
Each of these parameters plays a crucial role in determining the overall efficiency and performance of the heat exchanger, balancing the trade-offs between heat transfer effectiveness and pressure drop. Proper consideration of these factors ensures optimal design for specific operating conditions and thermal requirements.